Models equipped with Hitachi alternators:
APPLICATION
Model Hitachi No.
Datsun
1200 (1972)......................................LT135-13
(1973)...........................................LT135-38
510 (1972)......................................*LT135-13
- Datsun (1972-73)
- Chevrolet LUV (1972-73)
- Subaru (1972-73)
CHANGES, CAUTIONS, CORRECTIONS
BATTERY INSTALLATION, BATTERY CHARGING, OR USING A BOOSTER BATTERY FOR ENGINE START - Reversed polarity or excessive voltage will result in extensive damage to alternator system. Note the following to prevent damage.
Battery Installation - Negative battery terminal must be connected to ground. Positive terminal must be connected to starter lead. DO NOT reverse battery leads.
Battery Charging - If a Quick Charger is used, both battery cables must be disconnected from the battery. DO NOT use a Quick Charger to provide starting voltage.
Booster Battery (For Engine Start) - Booster battery must be connected with negative lead to negative battery terminal and positive lead to positive battery terminal. DO NOT reverse battery leads.
DESCRIPTION
Hitachi alternators are conventional three-phase, self rectifying type alternators. Six diodes (positive and three negative) are used to rectify currentAPPLICATION
Model Hitachi No.
Datsun
1200 (1972)......................................LT135-13
(1973)...........................................LT135-38
510 (1972)......................................*LT135-13
(1973).........................................LT150-058
521 Pickup (1972).............................LT135-13
610 (1973)......................................LT150-058
620 Pickup (1973)...........................LT135-138
240Z (1972)......................................LT150-05
1973............................................LT150-10
Chevrolet LUV (1972-73)......................LT130-83
Subaru
1300 &1400 (1972-73)......................LT135-20
* - Optional, LT150-05
SPECIFICATIONS
Alternator Amp* Volts
LT130-83...............................22.............................14
LT135-13...............................28.............................14
LT135-138.............................28.............................14
LT150-20...............................21.............................14
LT150-05..............................37.5...........................14
LT150-058............................37.5............................14
LT150-10..............................37.5............................14
* - Minimum
Nominal Output
Alternator Volts Volts
LT130-83...............................12.............................30
LT135-13...............................12.............................35
LT135-138.............................12.............................35
LT150-20...............................12.............................35
LT150-05...............................12.............................50
LT150-058.............................12.............................50
LT150-10...............................12.............................50
Resistance Values (Ohms)
Alternator Stator Cell Volts
LT130-83...............................0.13.............................4.3
LT135-13...............................0.17.............................4.4
LT135-138.............................0.17.............................4.4
LT150-20...............................0.20.............................4.0
LT150-05...............................0.17.............................4.4
LT150-058.............................0.17.............................4.4
LT150-10...............................0.17.............................4.4
illustration, and test as follows:
1) Detach connectors at alternator. Connect a test probe from voltmeter positive terminal to "N" or "BAT" terminal. Connect other test probe to ground. Check that voltmeter registers battery voltage.
2) Turn on headlights on high beam. Start engine and increase speed to approximately 1000 RPM and observe voltmeter. If voltmeter registers below 12.5 volts, alternator is defective. If above 12.5 volts, alternator is good.
Subaru Models - 1) Connect a voltmeter and leads to battery as shown in illustration. Operate the alternator and turn off the switch "SW" when alternator speed reaches approximately 800 RPM. Increase speed in small increments while watching voltmeter deflection and read alternator speed when at 14 volts. Speed should be approximately 1000 RPM.
2) Next, make test connection using a 30-50 Amp variable resistance, battery, ammeter, and voltmeter as illustrated. Operate alternator with switch "SW-1" closed. When alternator speed reaches approximately 800 RPM, set the variable resistance to maximum and turn on switch "SW-2". Increase alternator speed while monitoring a constant 14 volts by adjusting resistance. Read current at 2500 RPM and 5000 RPM. Reading should be 21-25 Amps at 2500 RPM and 33-37 Amps at 5000 RPM.
2) NOTE - The following test will not indicate a open state of the diodes. Tester will indicate a continuity regardless of diode conditions. If tester leads are connected to the terminals with polarities reversed. Connect positive lead to tester alternator "N" terminal and tester negative lead to alternator "A" terminal. If continuity is observed on the tester, there exist one or more shorted positive diodes.
3) Next, connect tester positive lead to alternator "E" terminal and tester negative lead to alternator "N" terminal. If continuity is present it indicates that one or more of the negative diodes are shorted.
OVERHAUL
DISASSEMBLY
1) Remove nut and take out pulley, fan, and washer. Pull out spacer. Remove screws securing brush holder and brush holder cover. Withdraw brush and brush holder. NOTE - Leave "N" lead wire connected to stator coil lead.
2) Unscrew through bolts and separate front and reaer housings. Remove three set screws from bearing retainer and separate rotor from front cover. Pull rear bearing from rotor assembly, if replacement is necessary.
3) Remove diode cover and disconnect stator coil lead wire from diode terminal, using a soldering iron. Remove the diode assembly be unscrewing the terminal nut and diode-setting nuts. Remove stator from rear cover.
Rotor - Apply tester probes to slip rings of rotor. If ohm reading is within specifications, rotor conduction is satisfactory. If not, a disconnection of field coil may exist. Next, apply probes to slip ring and rotor core, to check ground. If conduction exist. replace rotor assembly.
Stator - The stator is normal when there is conduction between individual stator coil terminals. When there is no conduction between terminals, cable is broken, replace stator assembly. If each lead wire of stator coil (including neutral wire) is not conductive with stator core, condition is satisfactory. If conduction exists, stator is grounded and must be replaced.
Diodes - 1) Perform a conduction test on all diodes, in both directions, using an ohmmeter. Test the conduction between each terminal and plate. Diode installed on "+" plate is a positive diode which allows current to flow from terminal to "+" plate only, current does not flow from "+" plate to the terminal. A diode installed on the "-" plate is a negative diode and allows current to flow form the "-" plate to the terminal only, current does not flow from the terminal to the "-" plate.
2) If current flows in both directions, the diode is short circuited. If current does not flow in either direction, the diode is open. If any diode is defective, replace the entire diode assembly (individual diodes are not serviceable).
Brushes & Brush Springs - Inspect movement of brushes for smoothness. Clean brush holder if necessary. Check brushes for cracks and wear. Replace if beyond limits shown. Check brush spring for corrosion and damage. Determine if springs exhibit proper tension. Test brush holder for continuity between each holder; replace if continuity exists.
Brush & Spring Data
Alternator Brush Wear Limit Spring Pressure*
LT130-83........................0.28" (7 mm).......................... .9-12.2 oz.
LT135-13........................0.28" (7 mm)........................ 8.8-12.3 oz.
LT135-138......................0.28" (7 mm)........................ 8.8-12.3 oz.
LT150-20........................0.28" (7 mm).......................... 9-12.3 oz
LT150-05........................0.28" (7 mm)........................ 8.8-12.3 oz.
LT150-058......................0.28" (7 mm)......................... 8.8-12.3 oz.
LT150-10........................0.28" (7 mm)........................ 8.8-12.3 oz.
* - Measured with .08" (2 mm) protrusion from brush holder.
521 Pickup (1972).............................LT135-13
610 (1973)......................................LT150-058
620 Pickup (1973)...........................LT135-138
240Z (1972)......................................LT150-05
1973............................................LT150-10
Chevrolet LUV (1972-73)......................LT130-83
Subaru
1300 &1400 (1972-73)......................LT135-20
* - Optional, LT150-05
SPECIFICATIONS
Alternator Amp* Volts
LT130-83...............................22.............................14
LT135-13...............................28.............................14
LT135-138.............................28.............................14
LT150-20...............................21.............................14
LT150-05..............................37.5...........................14
LT150-058............................37.5............................14
LT150-10..............................37.5............................14
* - Minimum
Nominal Output
Alternator Volts Volts
LT130-83...............................12.............................30
LT135-13...............................12.............................35
LT135-138.............................12.............................35
LT150-20...............................12.............................35
LT150-05...............................12.............................50
LT150-058.............................12.............................50
LT150-10...............................12.............................50
Resistance Values (Ohms)
Alternator Stator Cell Volts
LT130-83...............................0.13.............................4.3
LT135-13...............................0.17.............................4.4
LT135-138.............................0.17.............................4.4
LT150-20...............................0.20.............................4.0
LT150-05...............................0.17.............................4.4
LT150-058.............................0.17.............................4.4
LT150-10...............................0.17.............................4.4
TESTING
NOTE - Some testing is described as part of Overhaul procedure in this article. The following testing is performed with alternator on vehicle. |
| HITACHI ALTERNATOR ASSEMBLY |
ALTERNATOR SPEED TEST
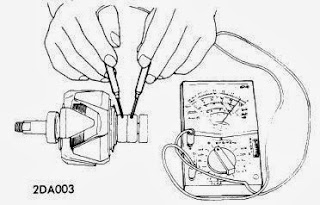
Datsun Models - Ensure battery has a full charge, then connect a 30-volt voltmeter as shown in  |
| ALTERNATOR TESTING - DATSUN |
1) Detach connectors at alternator. Connect a test probe from voltmeter positive terminal to "N" or "BAT" terminal. Connect other test probe to ground. Check that voltmeter registers battery voltage.
2) Turn on headlights on high beam. Start engine and increase speed to approximately 1000 RPM and observe voltmeter. If voltmeter registers below 12.5 volts, alternator is defective. If above 12.5 volts, alternator is good.
Subaru Models - 1) Connect a voltmeter and leads to battery as shown in illustration. Operate the alternator and turn off the switch "SW" when alternator speed reaches approximately 800 RPM. Increase speed in small increments while watching voltmeter deflection and read alternator speed when at 14 volts. Speed should be approximately 1000 RPM.
 |
| ALTERNATOR TESTING - SUBARU |
RESISTANCE & CONTINUITY TESTING
All Models - 1) Measure resistance, using suitable ohmmeter, across "F" and "E' terminals (rotor coil resistance). Rotor coil circuit is normal if resistance is 4 ohms. If resistance is higher than 4 ohms, there is poor contact between brushes and commutator. If no continuity exists between "F" and "E" terminals, there is either an open rotor coil circuit, brush sticking or a broken lead wire. If resistance is less than 4 ohms, it indicates rotor coil layer is short or grounded circuit. |
| ALTERNATOR OUTPUT TEST- SUBARU |
3) Next, connect tester positive lead to alternator "E" terminal and tester negative lead to alternator "N" terminal. If continuity is present it indicates that one or more of the negative diodes are shorted.
OVERHAUL
DISASSEMBLY
1) Remove nut and take out pulley, fan, and washer. Pull out spacer. Remove screws securing brush holder and brush holder cover. Withdraw brush and brush holder. NOTE - Leave "N" lead wire connected to stator coil lead.
2) Unscrew through bolts and separate front and reaer housings. Remove three set screws from bearing retainer and separate rotor from front cover. Pull rear bearing from rotor assembly, if replacement is necessary.
3) Remove diode cover and disconnect stator coil lead wire from diode terminal, using a soldering iron. Remove the diode assembly be unscrewing the terminal nut and diode-setting nuts. Remove stator from rear cover.
Rotor - Apply tester probes to slip rings of rotor. If ohm reading is within specifications, rotor conduction is satisfactory. If not, a disconnection of field coil may exist. Next, apply probes to slip ring and rotor core, to check ground. If conduction exist. replace rotor assembly.
Stator - The stator is normal when there is conduction between individual stator coil terminals. When there is no conduction between terminals, cable is broken, replace stator assembly. If each lead wire of stator coil (including neutral wire) is not conductive with stator core, condition is satisfactory. If conduction exists, stator is grounded and must be replaced.
 |
| BRUSH ASSEMBLY |
2) If current flows in both directions, the diode is short circuited. If current does not flow in either direction, the diode is open. If any diode is defective, replace the entire diode assembly (individual diodes are not serviceable).
Brushes & Brush Springs - Inspect movement of brushes for smoothness. Clean brush holder if necessary. Check brushes for cracks and wear. Replace if beyond limits shown. Check brush spring for corrosion and damage. Determine if springs exhibit proper tension. Test brush holder for continuity between each holder; replace if continuity exists.
Brush & Spring Data
Alternator Brush Wear Limit Spring Pressure*
LT130-83........................0.28" (7 mm).......................... .9-12.2 oz.
LT135-13........................0.28" (7 mm)........................ 8.8-12.3 oz.
LT135-138......................0.28" (7 mm)........................ 8.8-12.3 oz.
LT150-20........................0.28" (7 mm).......................... 9-12.3 oz
LT150-05........................0.28" (7 mm)........................ 8.8-12.3 oz.
LT150-058......................0.28" (7 mm)......................... 8.8-12.3 oz.
LT150-10........................0.28" (7 mm)........................ 8.8-12.3 oz.
* - Measured with .08" (2 mm) protrusion from brush holder.
REASSEMBLY
Reinstall diode assembly and stator to rear cover. Connect lad wires of stator coil to terminals of diode assembly. NOTE - Solder quicly to avoid damage to diodes. Reinstall diode cover. Reinstall rotor to front cover. Place assembly n vise and replace pulley and components. Insert and tighten housing through bolts. Assemble brushes to brush holder and insert holder into alternator. Perform as previously described.